A Review on Nature Conservation for Closed Land Fill Pdf
On this page:
- What is a Municipal Solid Waste Landfill?
- Learn about Municipal Solid Waste material Transfer Stations
- Regulations for Municipal Solid Waste material Landfills
- Publications and Guidance for Municipal Solid Waste product Landfills
What is a Municipal Solid Waste Landfill?
A municipal solid waste landfill (MSWLF) is a discrete area of land or digging that receives household waste. A MSWLF may besides receive other types of nonhazardous wastes, such as commercial solid waste, nonhazardous sludge, conditionally exempt small quantity generator waste, and industrial nonhazardous solid waste matter. In 2009, at that place were approximately 1,908 MSWLFs in the continental United States all managed by the states where they are located.
Non-hazardous solid waste is regulated nether Subtitle D of RCRA. States play a lead role in ensuring the federal criteria for operating municipal solid waste and industrial waste material landfills regulations are met, and they may set more stringent requirements. In absence of an approved country plan, the federal requirements must be met past waste facilities. The revised criteria in Championship twoscore of the Lawmaking of Federal Regulations (CFR) part 258 addresses vii major aspects of MSWLFs, which include the following:
- Location restrictions—ensure that landfills are built in suitable geological areas away from faults, wetlands, flood plains or other restricted areas.
- Blended liners requirements—include a flexible membrane (i.e., geo-membrane) overlaying two feet of compacted clay soil lining the bottom and sides of the landfill. They are used to protect groundwater and the underlying soil from leachate releases.
- Leachate collection and removal systems—sit on summit of the composite liner and removes leachate from the landfill for treatment and disposal.
- Operating practices—include compacting and covering waste frequently with several inches of soil.
These practices help reduce odor, control litter, insects, and rodents, and protect public health.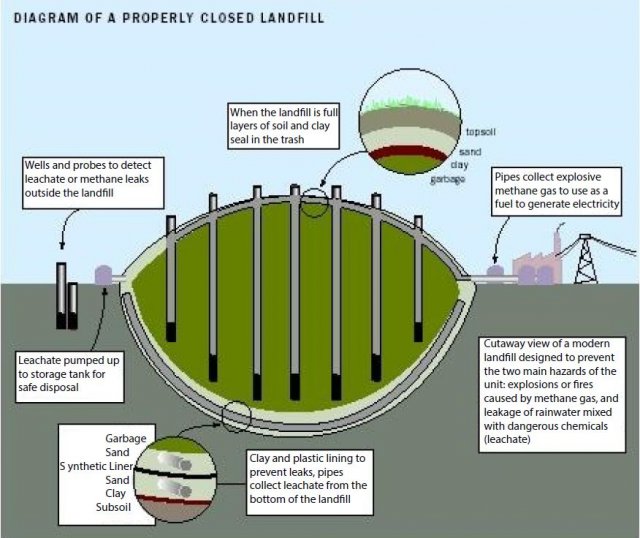
The image shows a cantankerous-department of a municipal solid waste product landfill. Click to enlarge. - Groundwater monitoring requirements—requires testing groundwater wells to determine whether waste materials have escaped from the landfill.
- Closure and mail-closure care requirements—include roofing landfills and providing long-term care of closed landfills.
- Corrective action provisions—control and clean up landfill releases and achieves groundwater protection standards.
- Fiscal assurance—provides funding for environmental protection during and afterward landfill closure (i.due east., closure and postal service-closure care).
Some materials may be banned from disposal in MSWLFs, including common household items like paints, cleaners/chemicals, motor oil, batteries and pesticides. Leftover portions of these products are chosen household hazardous waste material. These products, if mishandled, can be dangerous to your health and the environment. Many MSWLFs have a household hazardous waste product drib-off station for these materials.
MSWLFs tin can as well receive household appliances (i.e. white goods) that are no longer needed. Many of these appliances, such every bit refrigerators or window air conditioners, rely on ozone-depleting refrigerants and their substitutes. MSWLFs follow the federal disposal procedures for household appliances that utilize refrigerants. EPA has general information on how refrigerants can harm the ozone layer and consumer information on the specifics for disposing of these appliances.
Municipal Solid Waste Transfer Stations
Waste transfer stations are facilities where municipal solid waste (MSW) is unloaded from collection vehicles. The MSW is briefly held while it is reloaded onto larger long-distance transport vehicles (e.g. trains, trucks, barges) for shipment to landfills or other treatment or disposal facilities. Communities can relieve money on the labor and operating costs of transporting the waste to a distant disposal site by combining the loads of several private waste product drove trucks into a single shipment.
They tin can also reduce the total number of trips traveling to and from the disposal site. Although waste product transfer stations help reduce the impacts of trucks traveling to and from the disposal site, they can crusade an increment in traffic in the immediate surface area where they are located. If not properly sited, designed and operated they can cause problems for residents living most them.
A Regulatory Strategy for Siting and Operating Waste material Transfer Stations provides information about waster transfer stations and the deportment EPA has taken to address this issue.
Regulations for Municipal Solid Waste material Landfills
The table below provides links to final and promulgated rules pertaining to the operation and management of MSWLFs. Background information and technical support documents are also available for several rulemakings.
Rulemakings for MSWLFs
| Championship | Description | Engagement of last rule |
|---|---|---|
| Revisions to Criteria for MSW Landfills: Proposed & Final Rules, July 29, 1997 (PDF) (6 pp, 136 K, About PDF) | The Country Disposal Program Flexibility Human activity of 1996 (LDPFA) directed the EPA Ambassador to provide additional flexibility to canonical states for any landfill that receives 20 tons or less of municipal solid waste per day. The boosted flexibility applied to alternative frequencies of daily cover, frequencies of marsh gas monitoring, infiltration layers for concluding cover, and means for demonstrating financial assurance. The additional flexibility allows owners and operators of small MSWLFs the opportunity to reduce their costs of MSWLF operations while still protecting human health and the surround. This straight concluding dominion recognizes that these decisions are best made at the Land and local level and, therefore, offers this flexibility to approved States. | June 29, 1997 |
| Atomic number 82-Based Pigment Rule and Supporting Materials | Criteria for Classification of Solid Waste Disposal Facilities and Practices and Criteria for MSWLFs: Disposal of Residential Atomic number 82-Based Paint Waste material; Final Rule | June 18, 2003 |
| MSW Landfill Location Restrictions for Aerodrome Safety – Technical amendment | EPA amended the location restriction section in the Criteria for MSWLFs under Resources Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) to add together a note providing information about landfill siting requirements enacted in the Wendell H. Ford Aviation Investment and Reform Act for the 21st Century (Ford Human action). The amendment does non change existing criteria under RCRA with respect to siting MSWLF units. Background information for this notice is bachelor through Regulations.gov using docket number EPA-HQ-RCRA-2002-0034. More information can located using 67 FR 45948 and 67 FR 45915 at FederalRegister.gov. | October viii, 2002 |
| Alternative Liner Operation, Leachate Recirculation, and Bioreactor Landfills: Request for Information and Data, Apr 6, 2000 | EPA considered revisions to the Criteria for MSWLs (40 CFR role 258) regarding the use of culling liners when landfill leachate is recirculated and allowing the operation of landfills as more advanced bioreactors. EPA requested more than information on these types of landfill processes to go along with whatever revisions. Background information for this detect is available through Regulations.gov using docket number F-2000-ALPA-FFFFF. More information tin located using 67 FR 45948 and 67 FR 45915 at FederalRegister.gov. | April 6, 2000 |
Publications and Guidance for Municipal Solid Waste Landfills
The table below includes additional resource and guidance for the operation and management of MSWLFs.
Guidance Documents, Memos, Reports and Fact Sheets
| Title | Description | Date |
|---|---|---|
| Disposal of Domestic Birds Infected by Avian Flu: An Overview of Considerations and Options | Outlines disquisitional factors in the avian influenza disposal process and includes a variety of both on and off site disposal/handling options, data on cleaning and disinfecting disposal equipment, guidance on transporting infected materials for disposal, and contact information for local and country ecology, agricultural, health, and emergency response organizations. | August 11, 2006 |
| Final Rule: Management of Sure Cattle Origin Fabric Pursuant to the Substances Prohibited from Use in Creature Food and Feed | Alternate disposal methods for certain cattle origin materials is necessary, because of the Food and Drug Assistants'southward terminal dominion prohibiting the use of these materials in all animal feed, including pet food. | Apr 27, 2009 |
| Clarification of April vi, 2004 Memo on Recommended Interim Practices for Disposal of Potentially Contaminated Chronic Wasting Disease Carcasses and Wastes (PDF)(5 pp, 21.two K, Nearly PDF) | Memo to provide certain clarifications and revisions based on standing discussions. These practices are particularly advisable for landfills facing a relatively large number of carcasses from a particular culling or other event. | November 2004 |
| Recommended Interim Practices for Disposal of Potentially Contaminated Chronic Wasting Disease Carcasses and Wastes (PDF)(four pp, 39.8 Thousand, About PDF) | Memo to provide states and MSWLFs facility managers with options for the disposal of potentially contaminated chronic wasting disease carcasses and wastes in municipal solid waste landfills. | April 2004 |
| Geo-synthetic Clay Liners Used in Municipal Solid Waste Landfills | Fact sheet to provide data on geo-constructed clay liners (GCLs) and presents case studies of successful applications. | Dec 2001 |
| Landfill Reclamation | Fact sheet to describe how landfill reclamation tin exist used to expand MSWLF capacity. | July 1997 |
Source: https://www.epa.gov/landfills/municipal-solid-waste-landfills
0 Response to "A Review on Nature Conservation for Closed Land Fill Pdf"
Post a Comment